This issue brings you the application of 5-ALA (ALA) in potatoes.
In this study, it was described in detail that 5-ALA promoted vegetative growth and dry matter accumulation by increasing the relative content of chlorophyll in crops, thus increasing the number of potato forming per plant, the weight of potato block per plant and the percentage of commercial potato.

5-ALA (ALA) is a hydrocarbon of oxygen and nitrogen, and a common precursor of all porphyrin compounds. It is related to photosynthesis and respiration, and is a physiologically active substance that exists naturally in plants and is necessary for plant life activities. Its non-toxic side effects, easy to decompose, no residue.
At present, ALA has been synthesized and produced by a number of domestic scientific research institutions, and is widely used as a leaf fertilizer on greenhouse tomatoes, cucumbers, strawberries and other crops. However, the effect of exogenous ALA on potato growth and yield has not been reported in China. In this experiment, potato was used as the material to study the effects of exogenous ALA on potato growth and yield, and to explore the optimal application concentration and period of ALA in production, in order to provide theoretical basis and practical guidance for the promotion and application of ALA in potato production.
Materials and methods
1.1 Site Overview The experiment was conducted in the teaching and scientific research Demonstration Park of the College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Hexi University from April to September 2013. The local altitude is 1 420 m, the sunshine duration is 2 986~3 088 h, the frost-free period is 150~170 days, the average annual temperature is 7.6 ℃, the soil quality of the experiment site is clay loam, the previous crop corn, flat terrain, the same fertility, irrigation conditions are convenient. The soil basic fertility of the test site was 8.525 g/kg for organic matter, 0.584 g/kg for total nitrogen, 168.5mg/kg for available phosphorus, 38.41 mg/kg for available potassium and 89.67 mg/kg for available potassium.
1.2 Experimental materials The potato variety tested was "Atlantic Ocean", the virus-free varieties were selected, which met the national quality standard for improved varieties, and were provided by Wanxiang Denong Potato Company in Zhangye City, Gansu Province. 5-ALA (ALA) liquid fertilizer was provided by Applied Fungi Engineering Laboratory of Gansu Province.
1.3 Test methods A split zone design was adopted in the test, with ALA application concentration (Al 0 mg/L(CK), A2 100 mg/L, A3 200 mg/L, A4 300 mg/L, A5400 mg/L, A6 600 mg/L) as the main zone. The spraying period (B1 seedling stage (about 15 days after seedling emergence), B2 bud stage, B3 initial flowering stage) was selected as the secondary area, a total of 18 treatments were repeated for 3 times, the plot area was 16.5 m2(5 m × 3.3 m), and water was sprayed in control. In each treatment plot, 30 t/hm2 of decomposed farm manure, 300kg/hm2 of pure nitrogen, 210 kg/hm2 of phosphorus pentoxide and 150 kg/hm2 of potassium oxide were applied. 60% nitrogen fertilizer is used as base fertilizer, 40% is used as topdressing, phosphate fertilizer and potassium fertilizer are applied as base fertilizer at one time. The planting method of single ridge and double rows covered by mulch was adopted: ridge width of 70 cm, ridge height of 25 cm, ditch width of 40 cm, 2 rows per row, row spacing of 30 cm and plant spacing of 25 cm, density of 66,700 plants /hm2. Agricultural film with width of 100 cm and thickness of 0.008 mm was used for mulch. ALA was sprayed on the leaf surface, the liquid dosage was 3 000 L/hm2 each time, and each treatment was sprayed twice in 3 growth stages according to the corresponding concentration, with an interval of 20 days each time. Because ALA is volatile, choose to spray in the evening in clear weather, and other management is the same as field.
1.4 Measurement items and methods Growth period and growth period Record: the growth period and growth period of each treatment were observed [11(] sowing period, seedling emergence period, bud emergence period, initial flowering period, full flowering period, maturity period, harvest period). Field growth and development characteristics observation records: In the tuber growth period (25/07), 3 plants were randomly selected from each plot, and the plant height, number of main stems above ground, and fresh weight above ground and underground were measured. Measurement of yield and agronomic traits: 10 potato plants were randomly selected from each plot during the harvest period, and the number of potato forming per plant, the weight of potato block per plant, the average weight of potato block and the rate of commercial potato were measured [12]. Each district separately harvested, calculated yield.
1.5 Data processing and statistical analysis test results are expressed as measured average values; Statistical analysis of test data was performed using Excel 2007 and DPS 7.05 software (new complex range method).
Results and analysis
2.1 Effects of ALA on potato growth stage
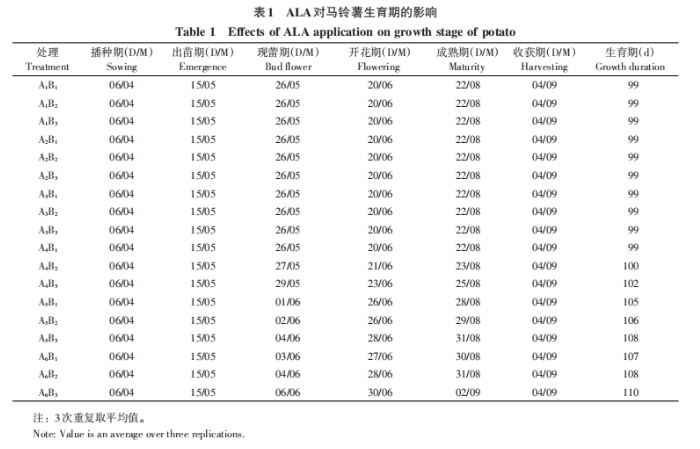
It can be seen from the above results that different concentrations of ALA and spraying periods have different effects on potato growth and growth periods. With the delay of spraying time, the growth period is delayed. The above analysis showed that when the concentration increased to 300 mg/L, the potato growth stage and growth stage would be delayed, and the effect was more obvious with the delay of spraying time.
2.2 Effects of ALA on potato plant traits
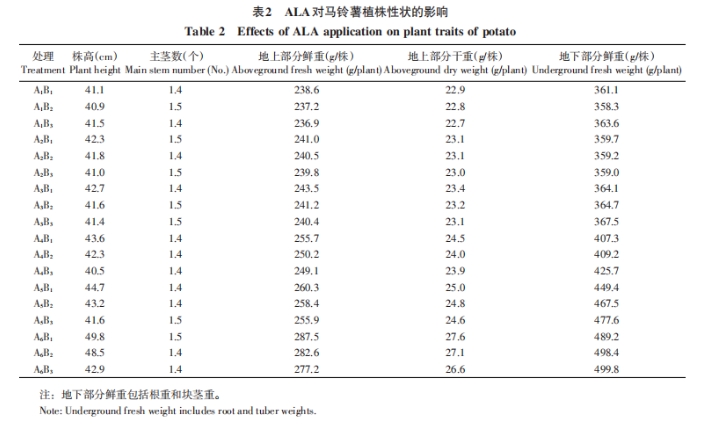
As can be seen from the above results, ALA can promote the growth of potato plants. The plant height increased with the increase of ALA concentration. Under the same concentration, the earlier the spraying, the more obvious the increase in plant height. The effects of ALA on above-ground fresh weight and dry weight showed the same trend as plant height. With the increase of ALA concentration, the above-ground fresh weight and dry weight gradually increased, and at the same concentration, the earlier the spray, the more obvious the weight gain. And with the delay of the spraying period, the more obvious the weight gain.
2.3 Effects of ALA on potato tuber traits
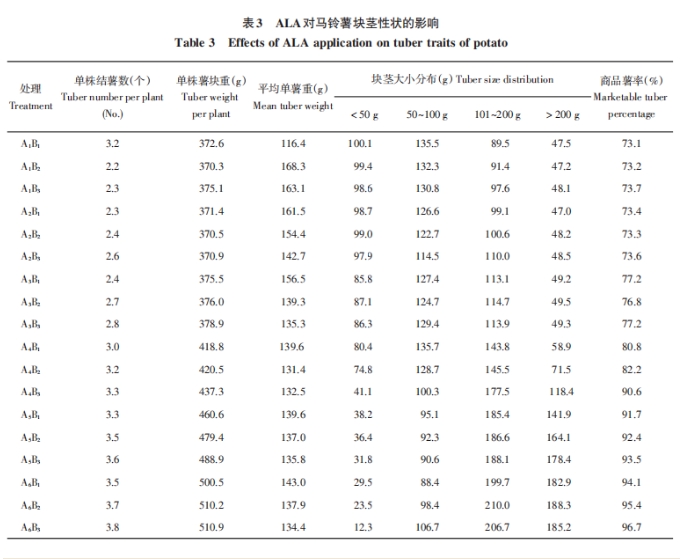
It can be seen from the above results that spraying ALA can promote the growth of potato tuber, increase the number of potato forming per plant and the weight of potato block per plant. The potato block weight of A4B3, A5B3 and A6B3 was 437.3, 488.9 and 510.9 g, respectively, which was 62.2, 113.8 and 135.8 g higher than that of A1B(3 375.1 g). ALA can also promote the yield of large potatoes and commercial potatoes.
Conclusion and discussion
In this period, the application of 5-ALA (ALA) in potato was studied in depth, and the results showed that:
1. ALA, as a multifunctional plant growth regulator, can promote crop growth, improve quality and increase yield. The effect on plant growth and increase yield depends on the application concentration and application period of ALA.
2. When the concentration is increased to 300 mg/L, the yield increase effect appears; When the concentration was between 300 and 600 mg/L, the yield increased with the increase of the concentration, and the earlier the spraying period, the more obvious the yield was, and the highest yield was reached when the 600 mg/L concentration of ALA was sprayed at the budding stage. 3. The main reason for increasing yield of ALA with a certain concentration is that spraying can increase the relative chlorophyll content of crops, which is conducive to photosynthesis, prolong the growth period, promote plant nutrient growth and dry matter accumulation, and thus increase the number of potato formation per plant, the weight of potato block per plant and the rate of commercial potato.
In summary, ALA can promote the growth of potato plants; The plant height increased with the increase of ALA concentration. · ALA spray can promote the growth of potato tubers, increase the number of potato forming per plant and the weight of potato block per plant. · The yield increases with the increase of concentration, and the earlier the spraying period, the more obvious the yield increase effect
· It is beneficial to photosynthesis, prolongs growth period, promotes vegetative growth and dry matter accumulation of plants, and increases the number of potato forming per plant, the weight of potato block per plant and the percentage of commercial potato.